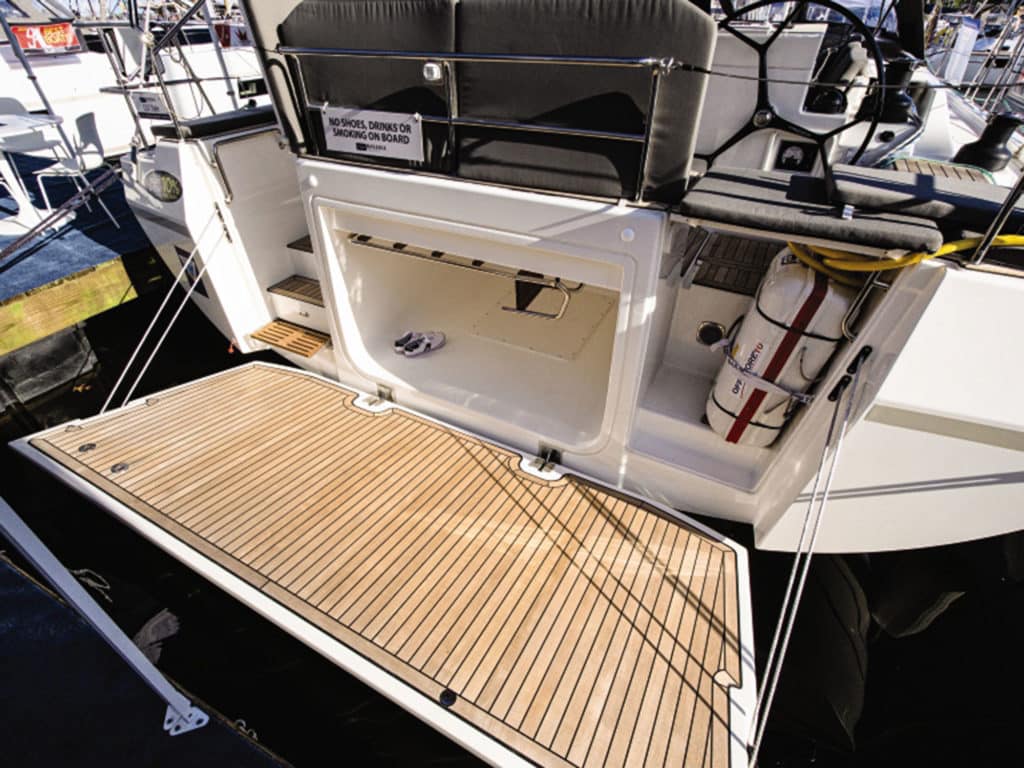
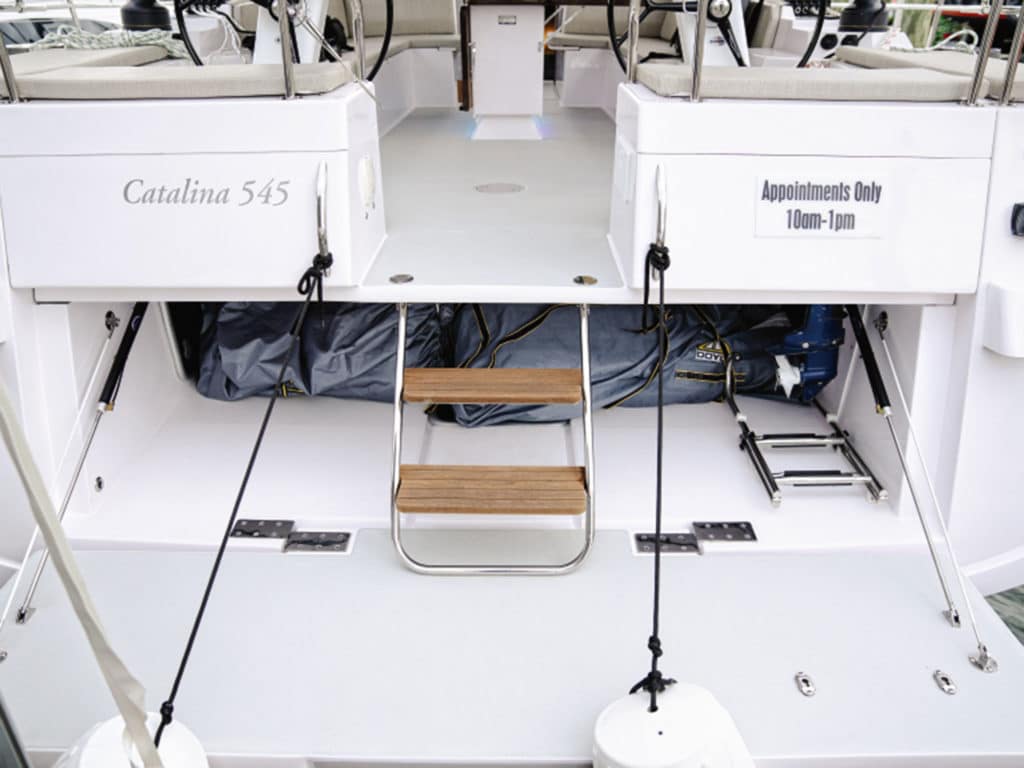
During this past October’s Boat of the Year competition at the US Sailboat Show in Annapolis, Maryland, the judges became quite familiar with the concept of “garages.” That is, a large stowage area under the cockpit for dinghies as long as 10-plus feet, as well as hard-bottomed RIBs with sizable outboard motors, and even consoles. They are accessed by fold-down doors or transoms that double as swim or launch platforms. During our evening deliberations, we three BOTY judges—Ralph Naranjo, Ed Sherman and me, along with CW editors Mark Pillsbury and Herb McCormick—began to speculate what other developments in carrying dinghies might have emerged alongside this particular innovation.
At the risk of being anticlimactic, the best answer is: none.
The other options, beyond the garage, are familiar, but there is not one unanimous choice that suits all sailboats. The decision tree begins with the mothership, and the best choice is dictated mostly by its size and design. So if you haven’t bought your cruising sailboat yet, eye each candidate with its suitability for carrying the dinghy. But if you’re committed to your current boat, you’ll have to make do.
Tow It
This maneuver is OK for sheltered waters but not advisable in rough conditions, even on coastal forays. There must be a provision for securing the dinghy out of the water. If it fills with water, you might have to cut it loose before it endangers your boat. Losing a dinghy is painful.

Select the painter wisely. While it would be ideal if it floated, common polypropylene quickly degrades in the sun. Three-strand or braided nylon is strong and durable. Beyond capsize or filling with spray or rainwater, a third risk is having the painter foul the propeller. Years ago, while entering Chesapeake City harbor, we ran aground. Instinctively I threw the transmission into reverse and turned to wave off the boats following us. Minutes later, while looking for alternative places to anchor, I noticed that the dinghy was gone. We expected to find it adrift, but no such luck. Then we saw it, totally submerged half under the boat. Yep, the painter fouled the prop, which yanked it underwater. What an idiot! Worse, the dinghy’s bow eye smacked a prop blade, bending it badly. The lesson? Shorten the painter for tight maneuvers.
Stow It
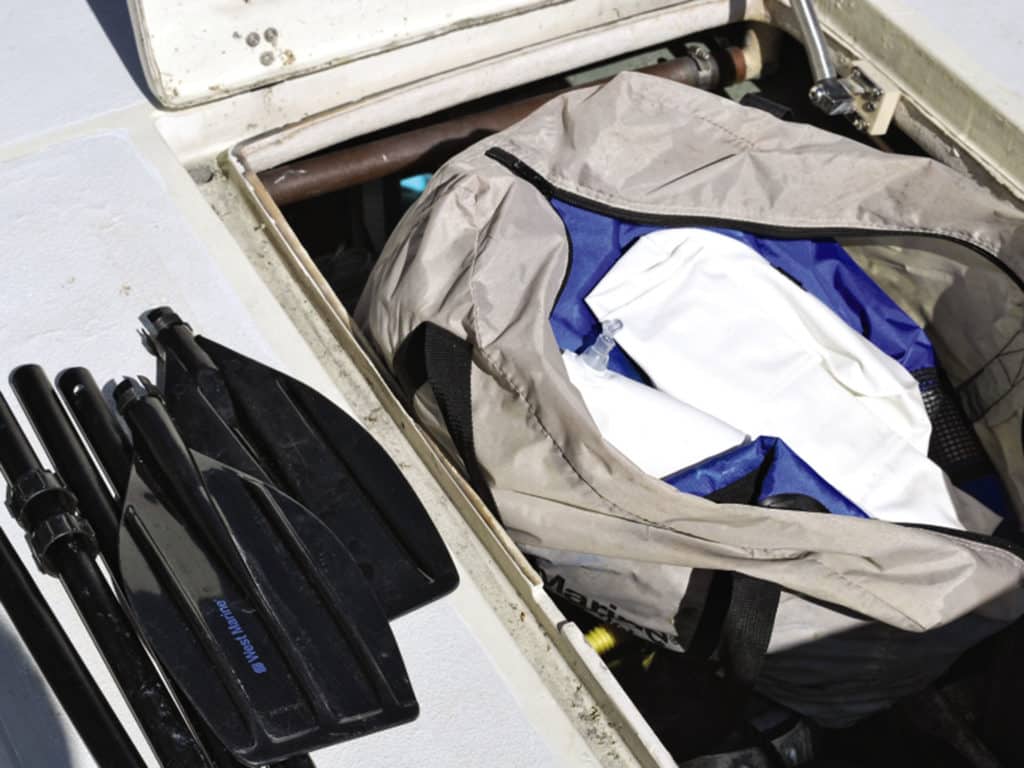

If your tender is inflatable, it might be possible to deflate it to stow in a locker (this rules out RIBs, whose fiberglass or aluminum hulls won’t fit in the lockers of most boats). The one-time commodore of the Ida Lewis Yacht Club in Newport, Rhode Island, to which I once belonged, did this on his Wanderer III replica/sistership.
During one club cruise, upon arrival at an anchorage, I watched from our boat as he retrieved his deflated dinghy from a seat locker, laid it out in the cockpit, and began to inflate it with the familiar foot pump. It took perhaps 10 minutes or so. A 12-volt electric pump would’ve sped up the process. When finished, he tossed it over the side, secured the painter, helped his wife board, and then rowed ashore.
Granted, range in such a dinky dink is severely limited; this skipper eschewed even a small outboard, and inflatables do not row well. But in the right location, it is a means of getting ashore.
Lash It

Lashing down a dinghy on deck has long been a go-to option on many cruising boats. It’s dependent on having adequate space available between the mast and cockpit enclosure (dodger or windshield) or between the mast and foredeck. The latter is less preferred, and both require that sail- and boat-handling functions, such as reefing and anchoring, are not compromised.
In this instance, you need to figure out a means of deploying and retrieving the dinghy beyond picking it up with brute strength and flinging it over the side. A four-point bridle with a lift point at the center of gravity enables lifting more or less horizontally. For mechanical advantage, a halyard led to the lift point on one end and to a mast winch at the other will generally get the job done; the main difficulty is pushing the dinghy outboard over the water. A helper on the side deck, perhaps aided by a boat hook, will make the job easier and hopefully avoid a messy situation.
Minutes later, we noticed the dinghy was gone. Yep, the painter fouled the prop, which dragged it underwater.
The dinghy can be secured by multiple wraps of line to handrails port and starboard. Tighten well or use ratchet straps. Oars can be tied in as part of this package, along with an outboard motor set on the familiar rail mount. If it’s too heavy to hand down to a waiting dinghy in the water, consider an outboard-motor lift installed at the stern that employs a block and tackle to safely lower and raise the outboard off and onto its adjacent mount.
Lift It
Ah, davits. While davit hardware is somewhat expensive, this is a good option for coastal cruising. It is much safer than towing, and compared with lashing on deck, greatly simplifies launching and retrieval. If the boat has a swim platform, as more modern boats now do, it also simplifies getting in and out of the dinghy. Climbing down a transom ladder works too. And it’s usually OK to keep the outboard mounted on the tender’s transom, avoiding the often-tense business of lowering the motor from the deck to the dinghy.

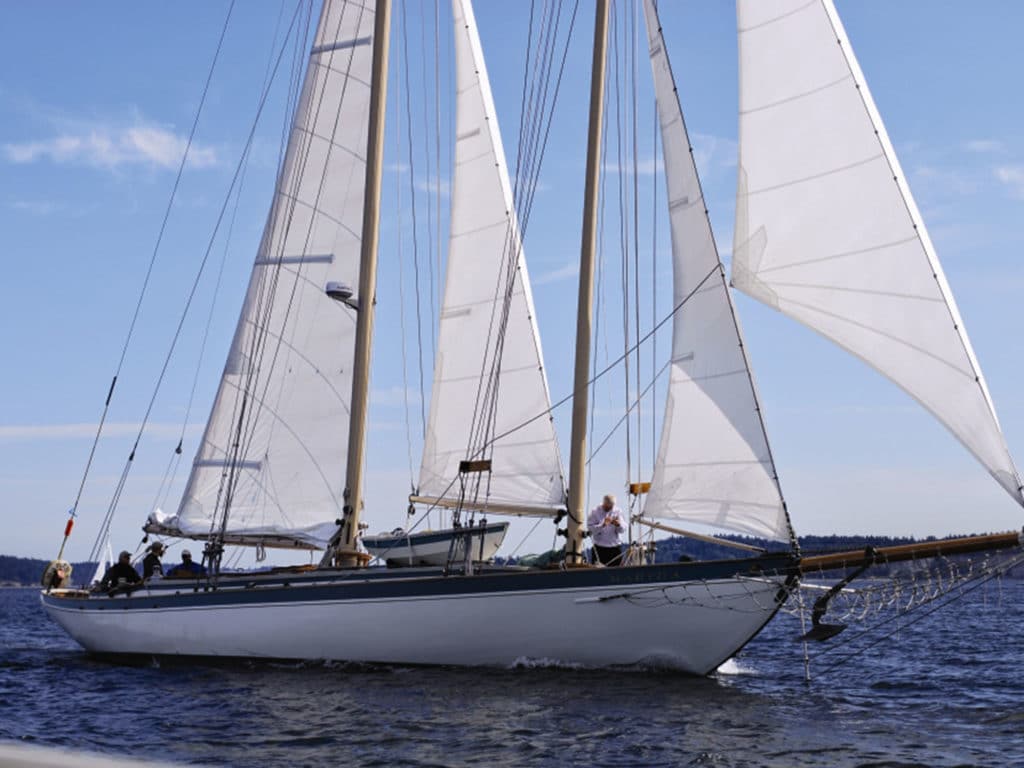
However, large breaking seas could rip off the dinghy and mangle the apparatus, possibly jeopardizing the big boat. And when docking, remember you’ve got baggage back there and don’t want to snag it on something, or bash a piling or other boat.

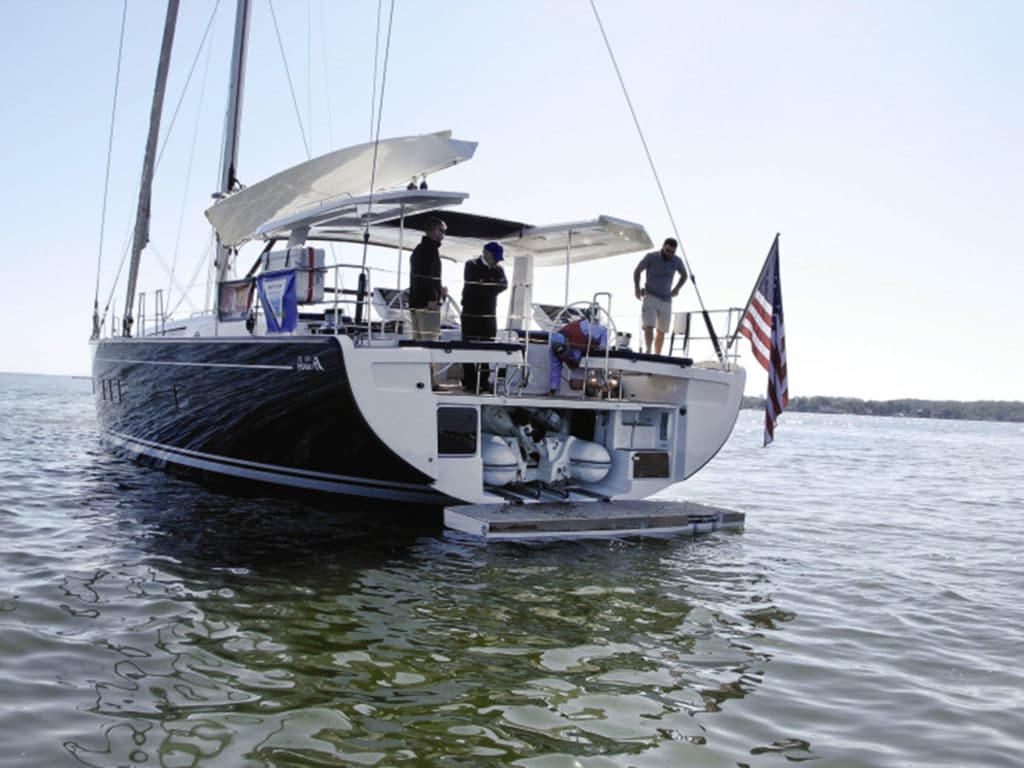
There is variety in the design of sailboat davits; for heavy loads, they mount on the afterdeck or transom, well reinforced below. With loads up to around 350 pounds, there are systems that can be mounted on a sturdy stern rail, and even kits to reinforce the stern rail.
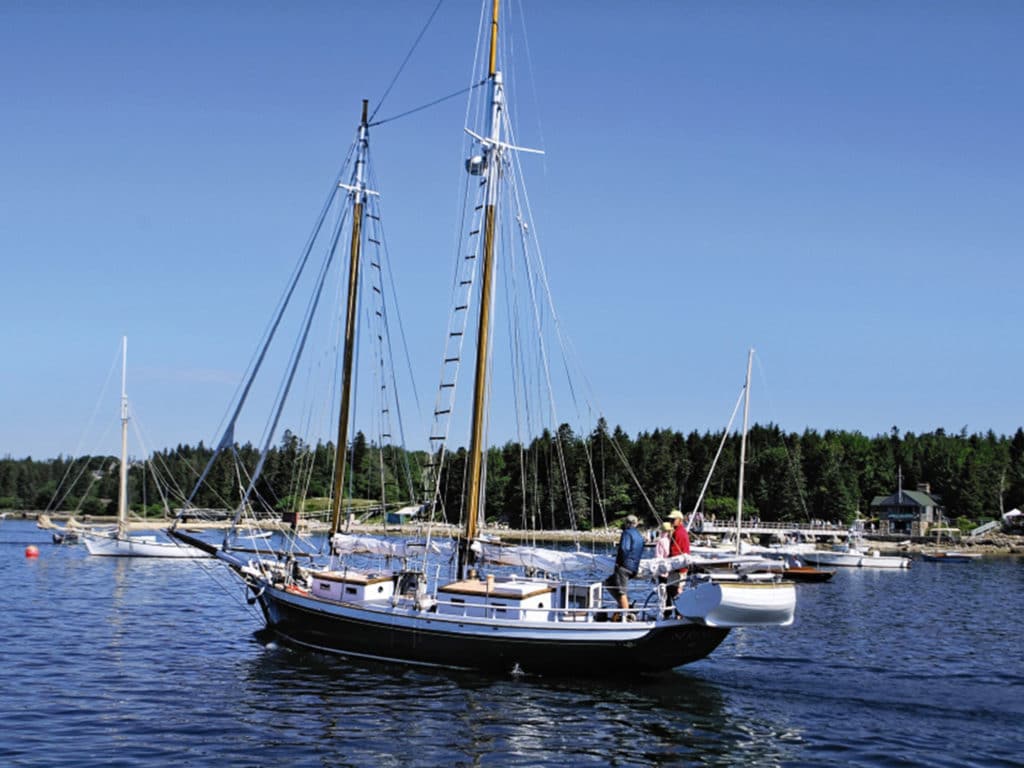
Some large traditional sailboats, such as schooners and windjammers, carry a shore launch in davits above the midship deck, but this won’t be a viable solution for most cruising sailboats.

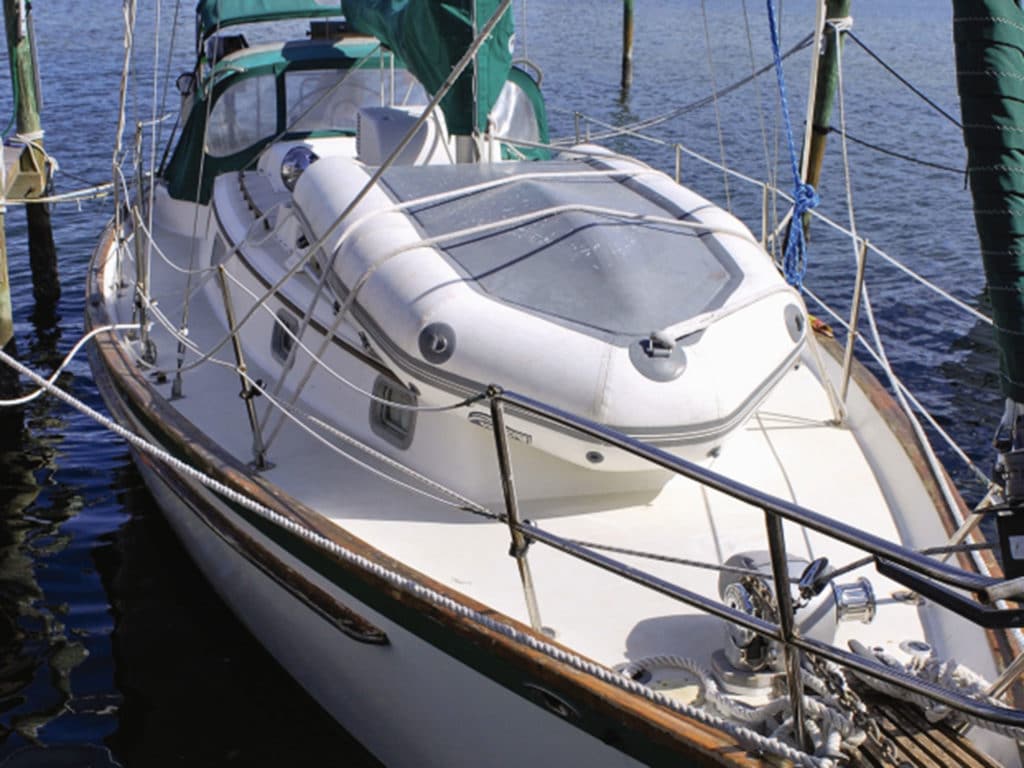
Park It
We’re back where we started, with the dinghy garage that was so popular in the 2020 BOTY competition. With so many larger boats carrying max beam aft to the transom, some designers and builders are incorporating the so-called garage for even fairly large RIBs with steering consoles under the cockpit floor, as mentioned. This is probably the safest, most secure way to carry a dinghy. Big boats such as the Hanse 675 and others employed garages with a variety of enclosure systems, most hydraulically activated. Sliding cradles that facilitate launching and retrieval with handheld controllers mean you don’t have to risk slipping a disc trying to grunt the beast aboard. Pretty slick! This isn’t something you could retrofit to an older design, but if you’re in the market for a new boat, it’s a feature well worth investigating.
Yachting journalist Dan Spurr has stowed dinghies on a long line of cruising boats he’s owned, ranging from a 28-foot Pearson Triton to a powerful Tartan 44.