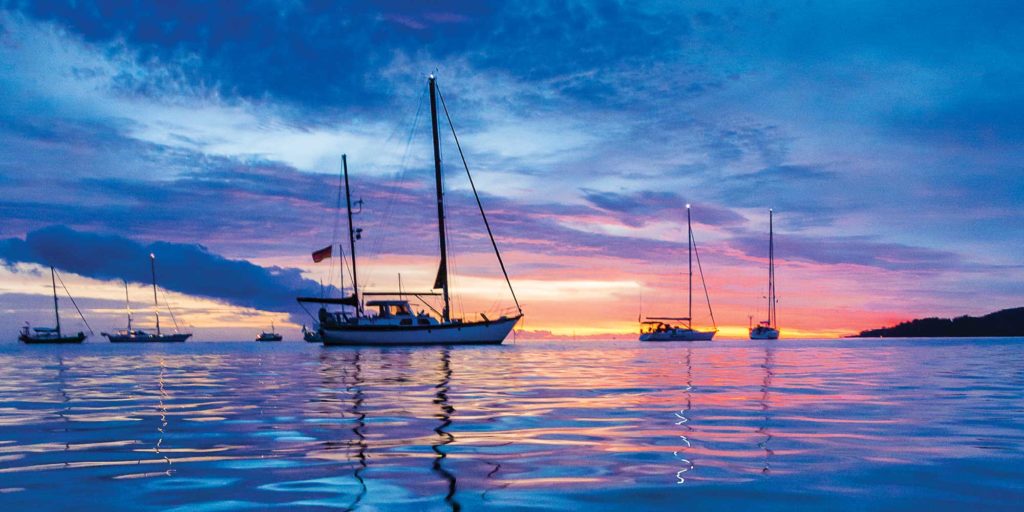
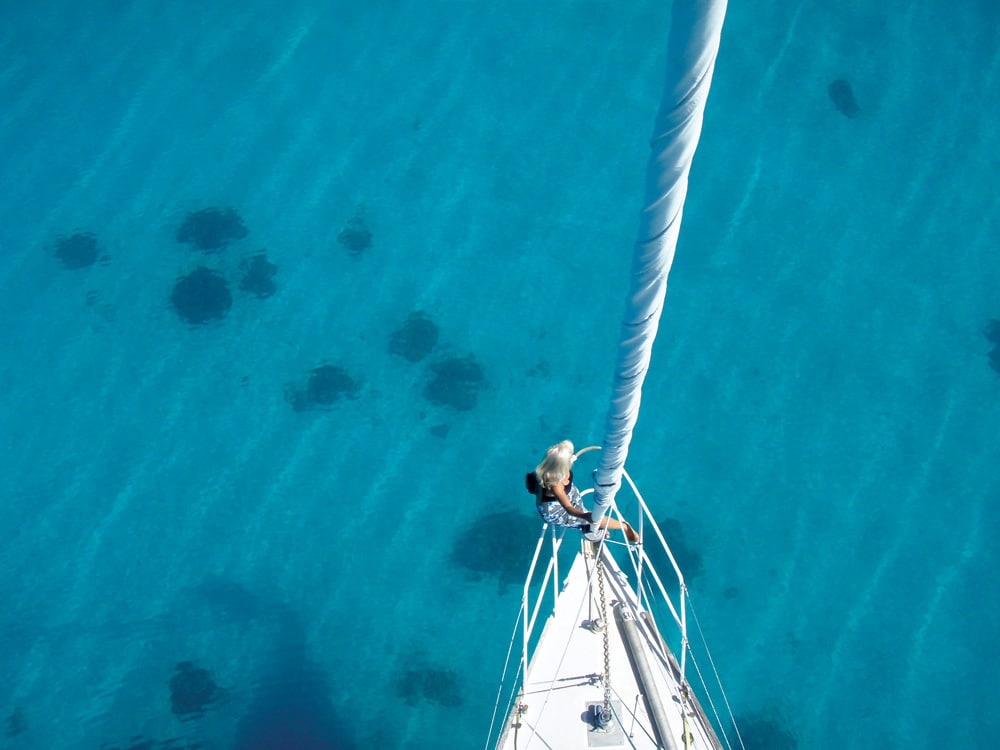
The definitions and delineations of a sea versus an ocean are complex, contested and best left to the learned geographers to debate. From a sailor’s point of view, excluding landlocked bodies of water, the rest of the brine is a contiguous path to glorious global adventure. Having said that, we do have our favorites. While the dreadful grind of the ice pack in the Far North and the towering graybeards of the Southern Ocean have their devotees, most sailing fantasies turn toward the seductive strum of the ukulele, the swaying palms and the white-sand beaches of the exotic South Pacific.
Ferdinand Magellan may have been a bit optimistic when he named a body of water that encompasses nearly one-third of Earth Mar Pacifico (peaceful ocean), for, like all oceans, it depends. The very size of the Pacific presents unique challenges, but so too do its strong currents, powerful storms, hazardous coral outcrops and remote low-lying islands.
Voyage Planning for Sailing the South Pacific
A successful Pacific passage will rely on meticulous planning, based on current information tempered with flexibility, because, by nature, cruising has it vagaries. But before one gets into the minutia of details, they should first step back and consider the bigger picture of sailing across the Pacific.
Is the vessel truly stem-to-stern, keel-to-masthead ready? Remember, a day’s work at the dock is worth a week’s under way. Is the dream and determination shared equally, or will the plan unravel with the first gale? Does a westward passage commit one to a circumnavigation, or are there strategic exit points? Does the voyage rely on a financial structure subject to change? Are you most comfortable as part of a rally, with a “buddy boat” or as a lone wolf?
Next is the paper chase. Gone are the whimsical days of letting the winds blow you where they may. The modern cruiser must be prepared in advance to face a host of legal requirements. First, ensure that every crewmember’s passport is as current as possible. Many countries will not issue visas to passports within six months of expiry. Next, list every country that you may wish to stop in and those in peripheral waters. Check the visa requirements carefully because the devil is in the details, especially if you have a multinational crew. Many countries require no visas if your stay is relatively short, or issue visas upon arrival. But some, such as Australia, will hit you with a hefty fine for showing up without one. Albeit increasingly expensive, cruising permits are normally obtainable upon arrival, but check the cruising websites and forums for current and accurate information. Make very high-resolution photocopies of your passports and ship’s papers. Bureaucrats love the pomp and splendor of shiny paper, and your precious original boat documents can stay safely on the vessel. If departing directly from U.S. waters, be aware that U.S. Customs does not normally issue a zarpe, or outbound clearance papers, yet these are required for entry into nearly any other nation. Download CBP Form 1300 and insist on a government stamp, any stamp. Be sure to have clear doctors’ prescriptions for every drug in the ship’s medical kit. What might be an over-the-counter medication in one country can be highly prohibited in another. Increasingly, foreign marinas demand third-party liability insurance. If you hope to further insure for damage and loss, check carefully the caveats relating to seasons and areas. If you plan to rent cars for touring, it is best to obtain an international driver’s license before departure.
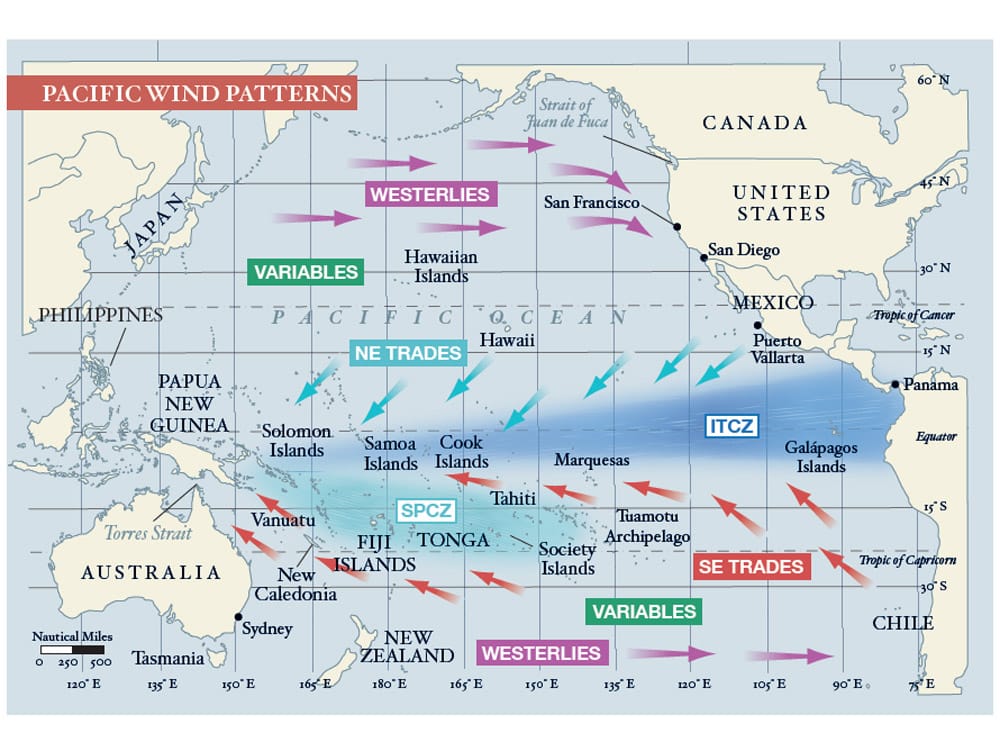
Familiarize yourself with the basic elements that will shape your course and schedule — the direction and timing of the prevailing winds, significant currents, cyclone seasons, the positioning of the intertropical convergence zone and the South Pacific convergence zone. Ascertain if the year of passage has been deemed an El Niño or La Niña year because these phenomena can affect the above.
West Coast sailors may depart from as far north as the Strait of Juan de Fuca, near Seattle, or dally south to Cabo San Lucas, Mexico, while awaiting the passage season. For European and East Coast sailors, the Pacific launching point is obviously the Panama Canal. The details of a canal transit are complex enough to warrant an article of their own, but relevant here is do not assume a quick passage, because during peak periods there can be several weeks of delay. Also, build in time to enjoy both the San Blas Islands, on the Atlantic side, and the Las Perlas Islands, on the Pacific side.

Pacific Sailing Routes
Although the official window for departures from Panama extends from February all the way to June, the trade winds tend to stabilize and strengthen as the year progresses. However, an early exit has many advantages. Leaving it until June allows only six months to transit up to 9,000 nautical miles before being forced to exit the cyclone belt at the western edge of the Pacific. This truncates the time to linger in favorite anchorages or tend to inevitable breakdowns and delays. Leaving as early as late January might technically put one out into the Pacific during the official cyclone season, but the statistical chances of a storm developing this far to the east are slim.
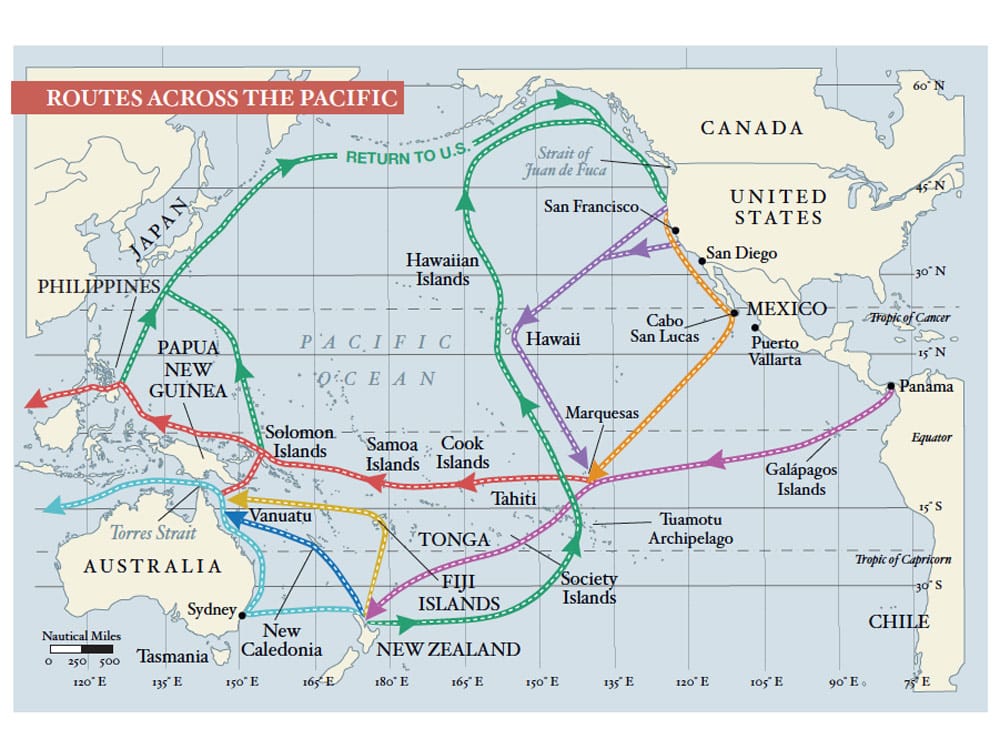
There are countless permutations of a westward passage, but the path dubbed the “Milk Run” is the most popular. Regardless of one’s plan for the western Pacific, this route passes by or through the Galápagos Islands, the Marquesas, Tuamotus and Society Islands (Tahiti).
The initial stage presents a challenge because the winds can be light and the currents contrary in the Gulf of Panama. It’s advisable to head slightly east of south when heading out of the Gulf; the western promontory is aptly named Punta Mala (Bad Point) due to its penchant for confused currents and squally weather.
Once well clear of the Gulf of Panama, fashion a southwestward course with a pronounced southern belly toward the Galápagos group. I once sailed a direct course for the Marquesas Islands that passed over the northern edge of the Galápagos. I paid for this foolishness by spinning in lazy circles for five excruciatingly long days. Given the early time of the year, I would have been better served by passing several degrees south of the island group. Because the intertropical convergence zone (better known as the doldrums) is widest in the eastern Pacific, it is best crossed at the least oblique angle reasonable.
On another Pacific passage, I chose to head south for Bahia de Caraquez in Ecuador. Not only was the cruise down the Ecuadorian coast fascinating, the passage to the Galápagos from Salinas provided steadier winds than had we departed directly from the canal.
The cost and conditions of a stay in the Galápagos are forever changing. As an admittedly stubborn form of protest, I sailed right by them on two different occasions. On the third, my wife, Diana, put her sea boots down and demanded we stop. Even with a limited stay and restricted access, we were treated to one of Earth’s most unique and fascinating natural habitats.
The 3,000-mile passage from the Galápagos to the Marquesas will probably be the longest of your sailing career. If you can focus on the journey instead of the destination, it might also be the most memorable. Many modern sailors tend to fill the Pacific void with a frenetic schedule of radio nets, emails and obsessive navigational updates. Others soak up the rare opportunity to commune deeply with nature, and experience a rare solitude and reaffirming self-reliance, which I believe to be the core virtues of bluewater sailing.
Counterintuitive to the landlubber but axiomatic to any old salt is that the rhumb line is often not the quickest route to a desired destination. Favorable winds mean speed, and the extra distance in search of them is usually well rewarded. When transiting from the Galápagos to the Marquesas, by first heading south-southwest down to 3 to 4 degrees south latitude, one should reach the upper limits of the southeast trade winds, albeit possibly sporadic at this point. But as you proceed west-southwest toward 6 degrees south latitude and 100 degrees west longitude, they should increase in both strength and consistency. As you straighten course toward your chosen port of entry in the Marquesas, you should begin experiencing your best noon-to-noon runs because you will still have a southerly component in the trades. This puts you on a broad reach, a point of sail most boats excel in. The farther west one heads, the more easterly the trades become until you are eventually running dead downwind. This tends to be a touch slower, with exacerbated rolling. Be sure to carry light-wind sails for the early portions of this journey, and equipment and sails suitable for downwind situations. That fortunate discrepancy you will notice between your speed on the log (i.e., through the water) versus the GPS speed (over the bottom) is compliments of the South Equatorial Current, which fortifies with the steadier trades.
There is only one shoal area along the route, which is well-charted (8 degrees 5 minutes N and 139 degrees 35 minutes W), and the islands are high and easily sighted from afar. Entrances to the main ports are open and well-marked, thus safely approached, a blessing for a fatigued crew. What the Marquesas Islands might lack in terms of white-sand beaches and aqua lagoons is more than made up for with a geography so dramatic as to be somewhat foreboding — towering rock spires, dense jungle and precipitous waterfalls. These islands have been protected from rampant development by a crushing remoteness and therefore arguably remain the cultural heart of Polynesia.
Passages between the islands are mostly clear and well-charted, but potentially windy. The anchorages tend to be open roadsteads, so anti-roll tactics and equipment come in handy. Yachts can clear in at Hiva Oa, Ua Pou or Nuku Hiva. Those first stopping in Fatu Hiva have met with mixed results, ranging from spot fines to official clearance. Yachts are no longer required to rush to Tahiti to extend their initial 30-day visa. Thus, with 90 days in pocket, you can divide your time between the Marquesas, Tuamotus and Societies more evenly than in years past.
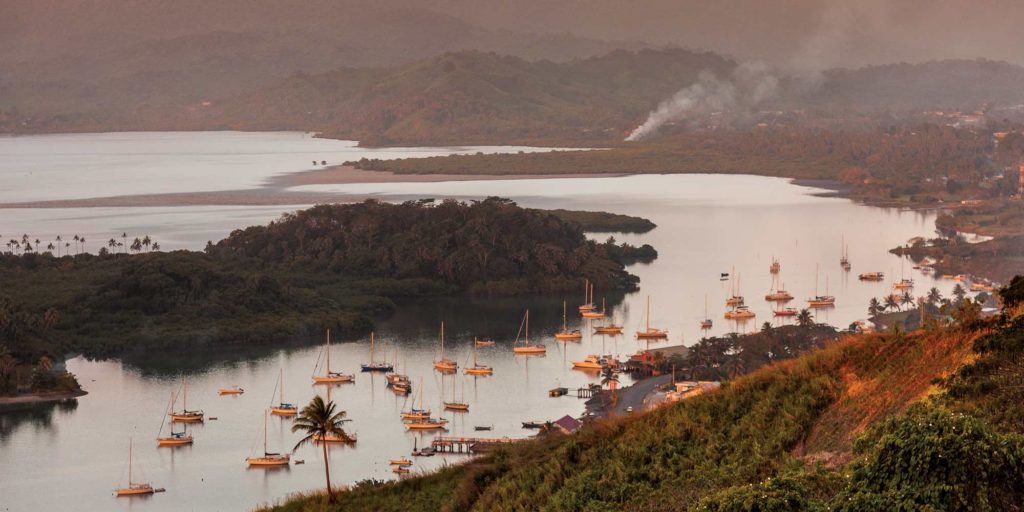

Encompassing an area larger than Western Europe, the Tuamotus are the longest chain of atolls in the world. Historically, they were known as the “dangerous archipelago,” and rightfully so due to a baffling maze of poorly charted reefs, low-lying islands and diabolically unpredictable currents. Even with the best of modern navigational equipment and weather forecasting, they demand the mariner’s absolute vigilance regarding watchkeeping, entry and exit from atoll passes, and anchoring techniques.
Those in a hurry to reach Tahiti tend to pass through the wider channels at the northern end of the chain, perhaps visiting Ahe, Manihi and the main center of Rangiroa. Others, with more time, make landfall far to the south and make their way up the chain via Makemo and the beautiful Fakarava Lagoon, enjoying a better angle off the wind on the short sail to Tahiti.

The Society Islands are divided into two groups: the Windwards, including Tahiti and Moorea, and the Leewards, with Huahine, Raiatea, Taha’a and, perhaps the most beautiful of them all, Bora Bora. They are all lush, high and ringed by azure seas. If early in the season, all are worth visiting. If time is short, be sure to at least attend the amazing group-dance competitions held in the buzzing capital of Papeete, celebrating Bastille Day on July 14.
North or South?
In Tahiti, the Milk Run divides into myriad possibilities. There is the northern route, for those planning to cross through the Torres Strait or into the Northern Hemisphere for the coming cyclone season, and the southern route, for those dropping south of the danger into New Zealand.

Although the majority of the South Pacific islands would remain unexplored, Tahiti is the earliest cutout for those needing to return to North America because its easterly location allows for a viable starboard tack through the southeast and northeast trades to Hawaii. The long but logical route from there is wheeling over the top of the North Pacific summer high and back south into U.S. West Coast waters.
While the land mass of the Cook Islands is a mere 100 square miles, its economic exclusion zone covers nearly 700,000 square miles of Pacific Ocean. One can only hope to draw a thin line through this scattered nation. For those on the southern route, the four- to five-day passage to Aitutaki or Rarotonga offers a predictable beam-to-broad reach right on the rhumb line.
En route to Niue lies one of two opportunities to experience the eeriness of anchoring in the middle of a featureless ocean (the other being the Minerva Reefs between Tonga and New Zealand). Beveridge Reef is a sunken atoll with not a skerrick of land awash at low tide, yet it offers anchorable depths within.
Niue is a raised coral atoll and geographically rare in the South Pacific. As anchoring depths are prohibitive, deep moorings are available. Keep in mind that it is an open roadstead vulnerable to dangerous swells. If the wind even hints at going west, as it occasionally does, get out immediately.
To break up the 1,200-nautical-mile haul to American Samoa from the Society Islands, the northern fleet usually takes a break in the remote and uninhabited atoll of Suwarrow, also known as Suvorov. The pass is challenging, as is the anchoring. But those who dare will be treated to one of the wildest places left on this planet.
From this point west, both the northern and southern fleet enter into the South Pacific convergence zone, a dangling arm of the intertropical convergence zone that extends from the Solomon Islands in an east-southeast direction. The South Pacific convergence zone drifts with some seasonal predictability (more to the north from December to May and the south from June to November), but is also influenced by larger weather anomalies. It tends to shift to the northeast in El Niño years and southwest in the La Niña phase. Generally, it is an area of enhanced convection resulting in a frustrating mix of cloud cover, line squalls and calms.
The list of interesting stops from here west includes Tonga, Wallis and Futuna, Fiji, Vanuatu, New Caledonia, Tuvalu, Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea. Nevertheless, those planning to sail directly through Torres Strait into the Indian Ocean cannot afford to dally. They should be through the Torres by late August or early September in order to cross the entire Indian Ocean into South Africa before the cyclone season begins sometime in late November. A popular alternative is to pass south to a good cyclone hole on the Australian coast, such as Cairns or Port Douglas, and backtrack up to the Torres Strait at the beginning of the next safe season.
Keep in mind that an east-to-west circumnavigation does not demand a route through the Torres. I once circumnavigated by passing north of Papua New Guinea, avoiding the Southern Hemisphere cyclone season, taking in Palau, the Philippines, and Borneo before dropping back into the Southern Hemisphere for the Indian Ocean passage to southern Africa. Any destination north of 10 degrees south latitude will keep you out of harm’s way, albeit without the steady assist of those lovely trade winds.

Those on the southern route can linger through Tonga or Fiji until well into November and still safely make New Zealand shores before any tropical depressions threaten. Most cruisers heading for New Zealand do not venture as far west as Vanuatu or New Caledonia on the assumption that they can easily fetch them on their way north the following season.
Unanimous acclaim for the beauty of the northern Tongan groups of Niua, Vava‘u and Ha‘apai makes some time here mandatory, which harks back to my original advice to head out of Panama as early as safely possible. The southern contingent usually drifts south toward Nuku‘alofa, the capital, until it likes the long-range forecast for the passage to New Zealand. Many plan to hole up in Minerva Reef, getting a head start on the 1,100 miles to New Zealand, and depart there with the absolute latest weather predictions.
The reputation of this leg has more bark than bite, but it cannot be denied that tropical weather events drifting down from the Coral Sea and cold fronts coming up from the Southern Ocean have dramatic potential. One can expect winds from nearly every direction, starting with southeast trades on departure and potentially deep lows with strong southwesterlies shifting to northwesterlies when approaching New Zealand. Thus, the usual advice is to fall off the southeast trades and make some westing in anticipation of that southwest-to-northwest change. Not to be a contrarian, but I have made this passage more than a half-dozen times and believe it is better to hold to the east as far as wind and waves allow because if that southwest change does not occur, you might find yourself on the wrong side of North Cape, New Zealand, with contrary winds and confused currents. Although Norfolk Island is not a fully protected anchorage, many vessels that find themselves west of the rhumb line with foul forecasts to the south will shelter here until conditions improve.
It’s possible, albeit tedious, to return to North America from New Zealand. Vessels head out to the east from as far south as Tauranga hoping to catch the northerly limits of the westerlies until they fetch the longitude of the Austral Islands, then turn north for Tahiti. From there, they follow the route as previously described. From the outset of their voyage, some have planned to sell their yacht in New Zealand or Australia rather than carry on with a circumnavigation or a very lengthy sail back to the United States, especially if they are East Coast residents. Import duties, brokerage costs and currency exchange rates must be factored into this strategy. Is it heresy to suggest that another option is to ship the vessel back home? The initial estimates might seem staggering, but once compared to the escalating marina and maintenance costs, and the many windward months and miles home, the horror subsides.
Whatever your plan from here, through a combination of wind and will, you have done it. You, your crew and your splendid craft have spanned the mightiest body of water on Earth. You have immersed yourself in millions of square miles of salty solitude and self-reliance. You have absorbed the exotic cultures of Central Americans, Polynesians, Micronesians and Melanesians. And now, as only a seasoned mariner can, you truly understand why they call it the Big Blue.
Contributing editor, Alvah Simon, and his wife, Diana, are presently sailing New Zealand waters on their cutter Roger Henry, with occasional voyages to the South Pacific islands.
South Pacific At A Glance
- Dry Season: May-October
- Wet Season: November-April
- Cyclone Season: November-April. Active
- Cyclone Area: south of 10° S; west of 140° W
- Distance: Panama to Australia — 8,000 nautical miles
- Cultural Areas: Polynesia, Micronesia, Melanesia, Australia/New Zealand
References:
- World Cruising Routes by Jimmy Cornell
- noonsite.com (Virtually everything you will need to know on a current basis will be found on this comprehensive website.)
- Atlas of Pilot Charts — South Pacific, DMA/NOAA
- The Pacific Crossing Guide by Kitty Van Hagen
- Charlie’s Charts of Polynesia by Charles and Margo Wood
- Landfalls of Paradise by Earl Hinz and Jim Howard
- South Pacific Cruising by David Thatcher
- South Pacific Anchorages by Warwick Clay
- Rocket Guide to Vanuatu & New Caledonia
- Solomon Island Cruising Guide by Dirk Sieling
- New Zealand Coastal Cruising Handbook by Royal Akarana Yacht Club
- Lonely Planet South Pacific Travel Guide
Selected SSB/Ham WX Nets:
- Southbound Evening Net: 6516 kHz at 0100 UTC
- Panama Pacific Net: 8143 kHz at 1400 UTC
- Pacific Maritime Mobile: 21.412 MHz at
- 2100-2400 UTC
- Pacific Magellan: 8173 kHz at 1730 UTC
- Pacific Seafarers: 14300 kHz at 0300 UTC
- Namba/Sheila Net: 8101 kHz at UTC plus 11 hours
- Gulf Harbor Radio: 8116 kHz at 0715 local New Zealand time
- (There is a host of smaller and temporary VHF and SSB nets throughout the Pacific.)